research introduction: Optimal Trajectory Design for On-orbit Inspection Using Spherical Gaussian
日本語字幕有り
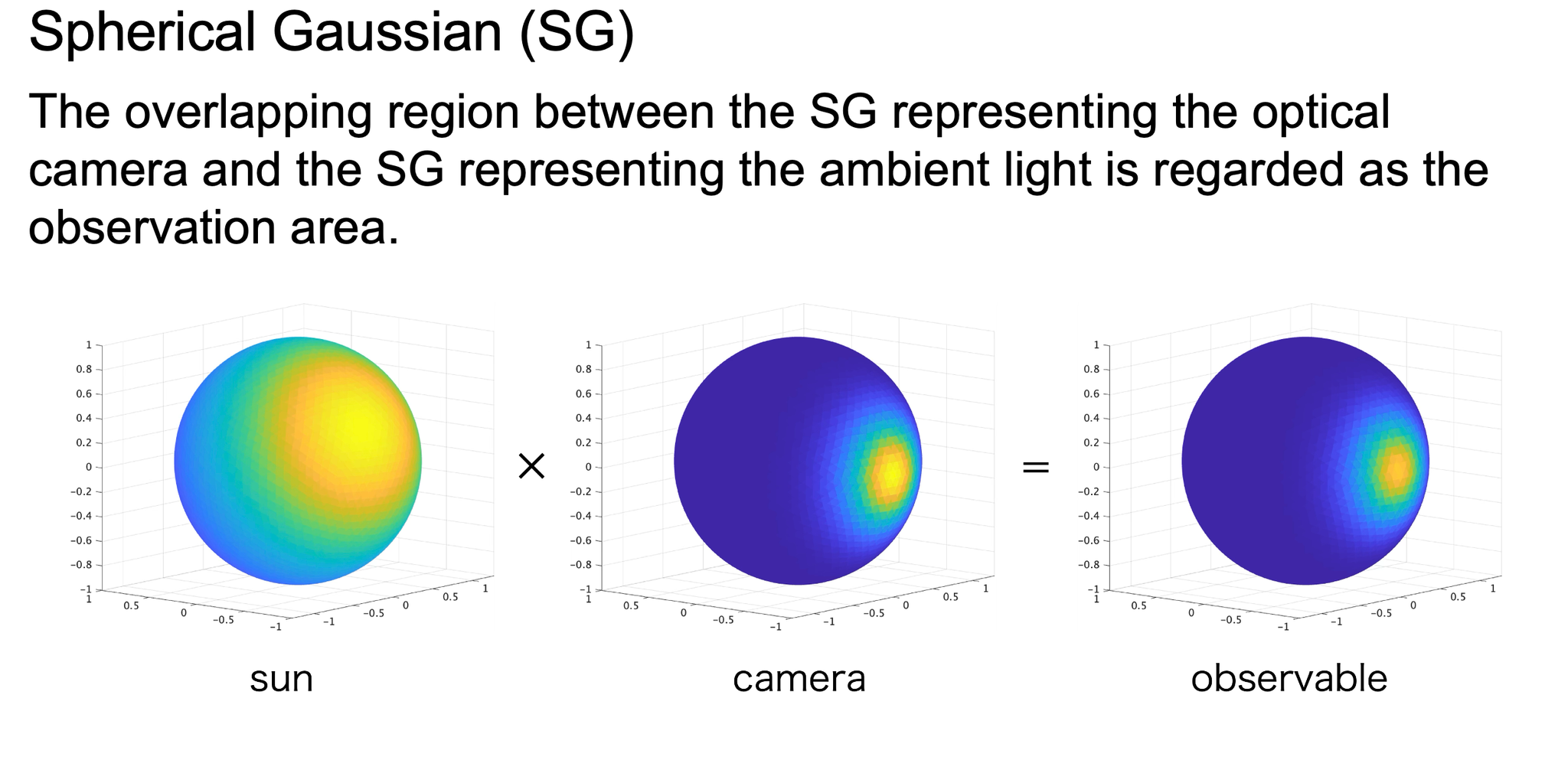
Optimal Trajectory Design for On-orbit Optical Inspection Using Spherical Gaussian
Takuto Nobuhara, Yasuhiro Yoshimura, Toshiya Hanada, Taku Izumiyama
本研究は,宇宙空間で人工衛星を点検するために,どのような軌道を飛べば効率よく対象を観測できるかを考えたものです.人工衛星の点検では,カメラで対象全体をできるだけ多く,しかも安全に観測する必要がありますが,距離や向き,太陽の当たり方によって見えやすさが大きく変わります.そこで本研究では,対象の見えやすさを球面ガウス分布という滑らかな数式で表し,カメラの視野や照明条件を同時に評価できるようにしました.この評価を使って軌道を最適化することで,燃料をあまり使わずに,対象表面を広く観測できる軌道を自動的に設計できます.数値シミュレーションの結果,従来の方法よりも効率よく点検できることが確認されました.
This study investigates how to design an efficient trajectory for inspecting a satellite in space using an optical camera. In on-orbit inspection missions, it is important to observe as much of the target surface as possible while maintaining safety, but the visibility strongly depends on the relative position, viewing direction, and illumination from the Sun. To address this, the study represents observation quality using a spherical Gaussian distribution, which provides a smooth and continuous way to describe how well different parts of the target can be seen, considering both the camera’s field of view and lighting conditions. By optimizing the satellite’s trajectory based on this observation model, the method can automatically find paths that achieve wide surface coverage with low fuel consumption. Numerical simulations demonstrate that the proposed approach enables more efficient and effective inspection compared with conventional methods.